Object-Oriented Programming Concepts
04 Apr 2024
Beginner
30.4K Views
5 min read

Learn via Video Course & by Doing Hands-on Labs
Java Programming Course
Object-Oriented Programming Concepts: An Overview
"Hello there! Have you ever considered how computer programs organize data? Go into the OOPs Tutorial, your resource for learning about Object-Oriented Programming Concepts. Discover how to separate tasks, arrange relevant data, and write efficient, modular code.What is object-oriented programming?
Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a programming approach that organizes software design around data, rather than functions and logic. An object is a data field that has distinct attributes and behavior.OOPs Concepts
Following are the OOPs Concepts:
- Class
- Objects
- Data Abstraction
- Encapsulation
- Inheritance
- Polymorphism
- Dynamic Binding
- Message Passing
1. Class
- A class is a data type that has been defined by the user.
- A class is similar to an object's blueprint.
- It is made up of data members and member functions that may be accessed and used by instantiating the class. It indicates the collection of attributes or methods shared by all objects of the same type.
- Examples: The Class Car defines methods like StartEngine and Accelerate, as well as characteristics like color and model.
2. Objects
- It is a fundamental unit of Object-Oriented Programming that represents real-world entities.
- An Object is a subset of a Class.
- When a class is defined, no memory is allocated; nevertheless, memory is allocated when the class is instantiated (i.e. an object is formed).
- An object has a name, a state, and a behavior.
- Each object contains data as well as code for manipulating the data.
- Objects can interact without knowing the specifics of each other's data or code; all that is required is knowledge of the type of message accepted and the type of response given by the objects.
- Examples: Object myCar is an instance of the Car class with its own color, model, and engine state.
3. Data Abstraction
- The method of hiding an object's internal characteristics from the outside world disclosing only necessary functions and information.
- This reduces programming complexity while also protecting data integrity by preventing unauthorized access or tampering.
- For example, a BankAccount class may hide its internal balance while providing deposit, withdrawal, and checking balance methods.
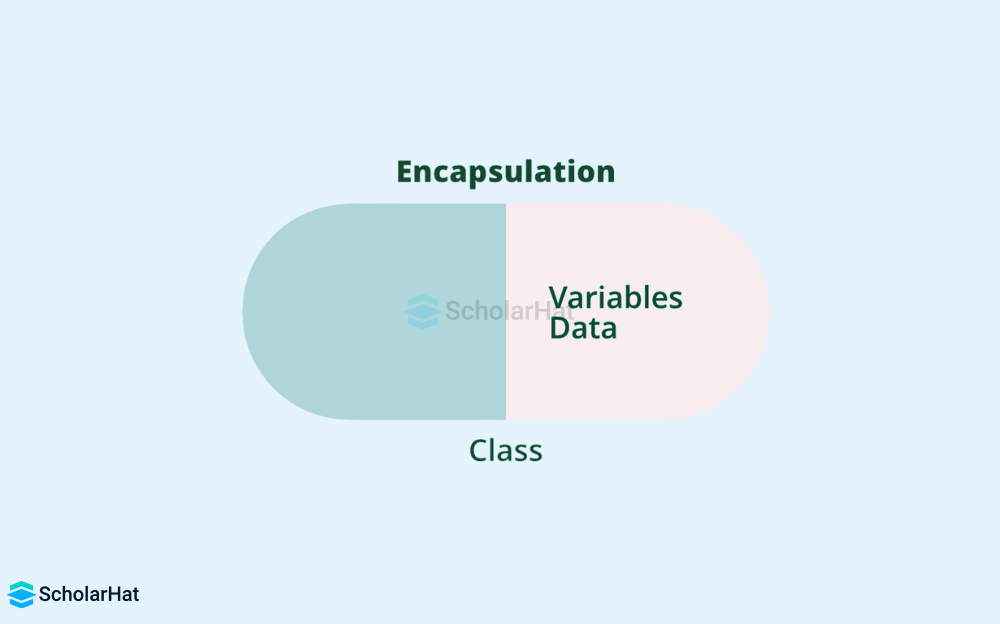
4. Encapsulation
- Data as well as the functions that operate on that data are combined into a single unit (class/object).
- This improves data security, modularity, & reuse.
- Example: A File class encapsulates data (file content) as well as file management methods (read, write, close).
Inheritance
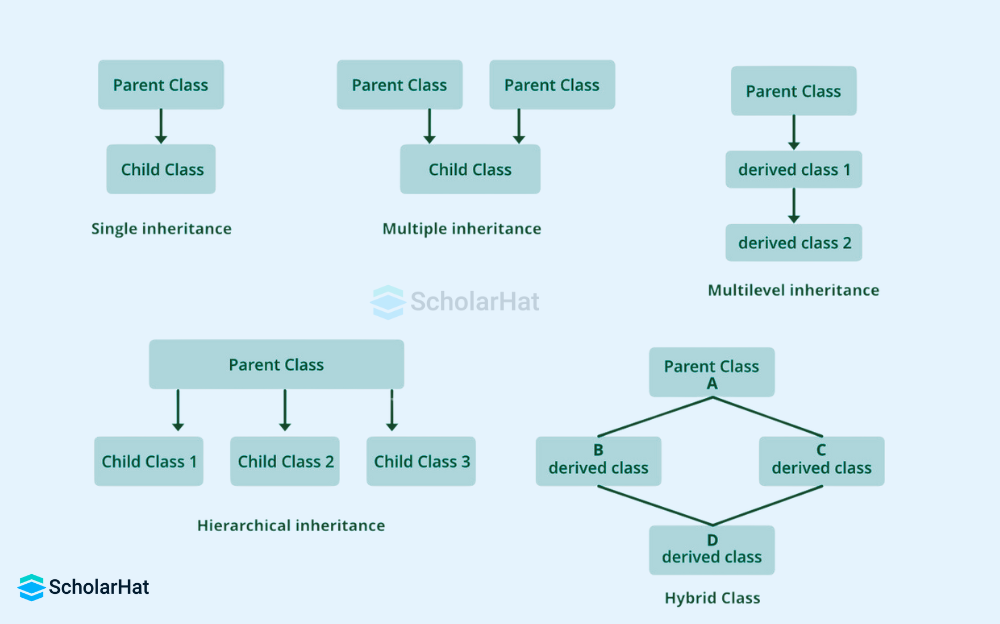
- Inheritance is a key component of OOP (Object-Oriented Programming).
- Inheritance refers to a class's capacity to derive features and traits from another class.
- We inherit properties from other classes when we write a class.
- So, when we build a class, we don't have to repeat all of the properties and functions because they can be inherited from another class that has them.
- Inheritance allows the user to reuse code as much as possible, reducing repetition.
- Examples: Class ElectricCar inherits from Car but adds specific methods like chargeBattery.
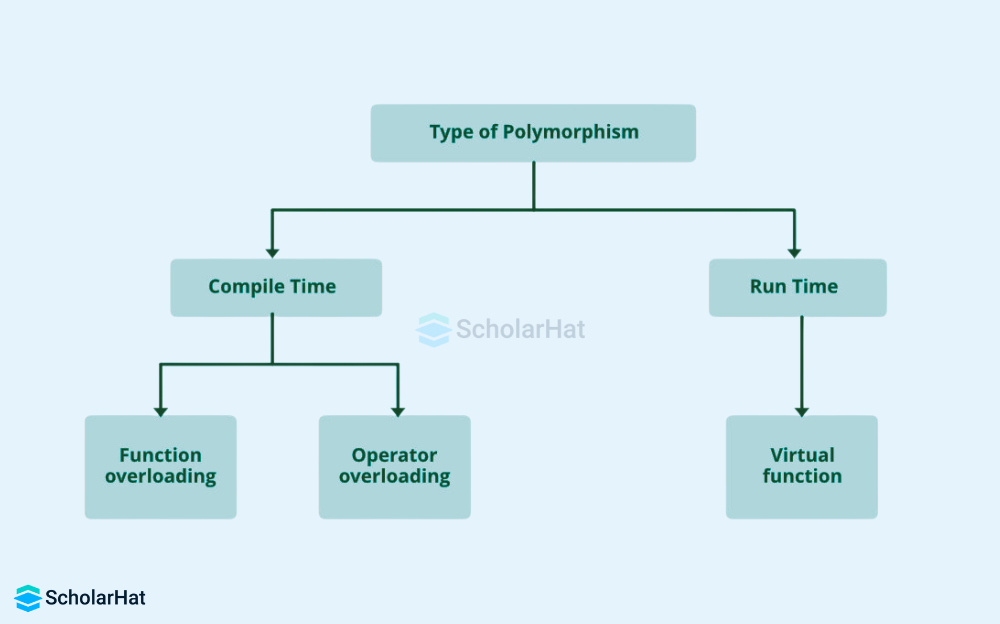
Polymorphism
- The ability of an entity (object or function) to change its form or behavior based on the situation.
- Treating objects of different types similarly provides flexibility and simplifies code.
- Examples: By modifying its behavior, a print() function can handle various data types like strings, integers, and objects.
Dynamic Binding
- At runtime, the process of binding a function call to the correct implementation based on the type of the object at that time.
- This allows for more flexible behavior and late-function binding.
- Example: Depending on the object calling it at runtime, the eat() function in Animal may have different implementations for Cat and Dog.
Message Passing
- In object-oriented programming, the communication method between objects.
- Messages (function calls) are sent between objects with data as arguments, activating certain behaviors.
- This encourages modularity and decoupling, resulting in more manageable and reusable code.
- Example: To initiate the window's close function, a Button object clicks on a Window object.
Why is object-oriented programming required?
- To simplify the development and maintenance of projects.
- To give a data masking function that is beneficial for security issues.
- Using object-oriented programming, we can tackle real-world challenges.
- It guarantees code reusability.
- It enables us to develop generic code that will function with a variety of data, eliminating the need to repeat fundamental code over and over.
Summary
Object-oriented programming (OOP) organizes software around data-packed objects with characteristics and actions. Classes (blueprints), objects (instances), and data hiding (protection) are key notions. Polymorphism adapts behavior based on context, whereas inheritance allows objects to inherit qualities from others. Object messaging encourages modularity and reusability. OOP simplifies development, increases security, and efficiently solves complicated problems.
FAQs
Q1. What are the 4 basics of OOP?
Object-oriented programming (OOP) allows objects to communicate with one another by utilizing four fundamental principles: encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism, and abstraction.
Q2. What is OOPS in simple words?
The concept of objects underpins object-oriented programming. Data structures, or objects, are defined in object-oriented programming, each with its own set of traits or attributes. Each object can also have its own set of processes or methods. Objects that interact with one another are used to create software.
Q3. What is an OOPS class?
A class is a blueprint for constructing objects (a specific data structure), giving starting settings for the state (member variables or attributes), and implementing behavior (member functions or methods) in object-oriented programming. The class keyword is used to build user-defined objects.
Q4. What is the full form of OOPS?
Object Oriented Programming System is the full form of OOPS.
Q5. What is the basis of encapsulation?
Encapsulation is a method for restricting direct access to some components of an object so that users cannot get state values for all variables of a specific object. Encapsulation can be used to conceal both data members and data functions or methods associated with a class or object that has been instantiated.



