25
AprUnderstanding Inheritance and Different Types of Inheritance

Java Programming Course
What is Inheritance?
Inheritance is a mechanism of acquiring the features and behaviors of a class by another class. The class whose members are inherited is called the base class, and the class that inherits those members is called the derived class. Inheritance implements the IS-A relationship.
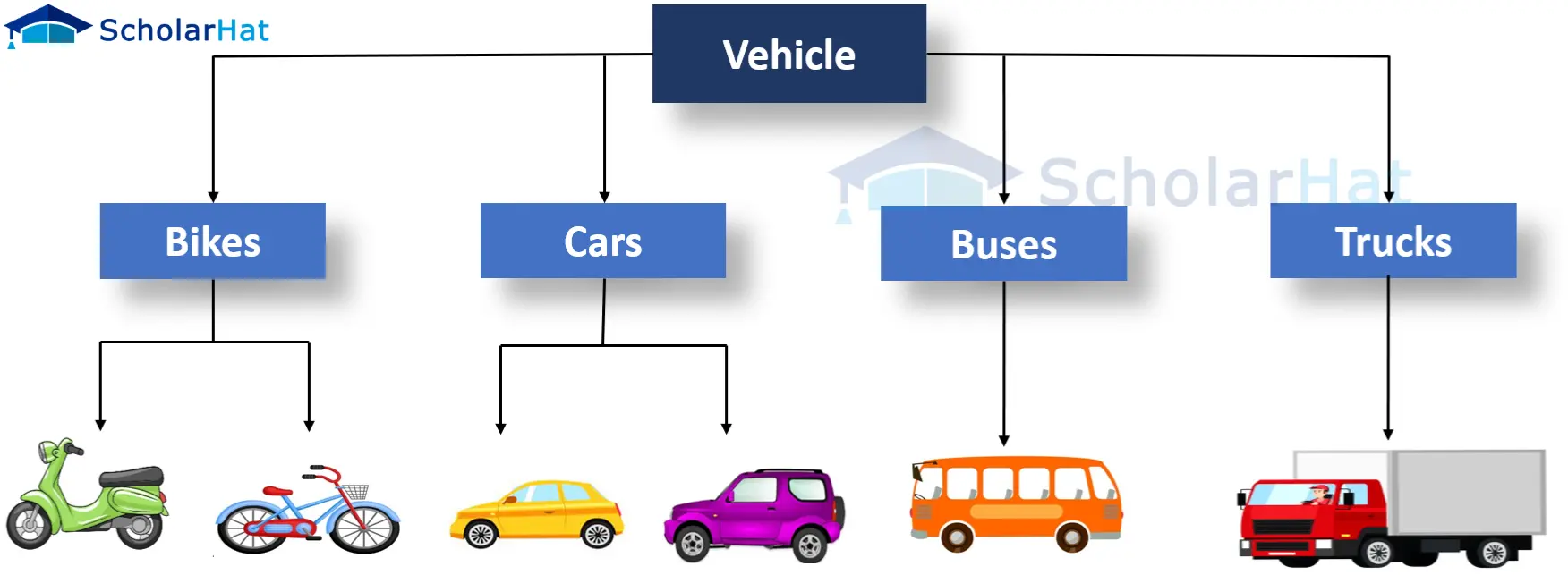
In the above figure:
- A car is a Vehicle
- A bus is a Vehicle
- A truck is a Vehicle
- A bike is a Vehicle
Inheritance is one of the core aspects of Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) and it provides a way of achieving code re-usability. It prevents the need to write the same code multiple times.
Different Types of Inheritance
OOP supports six different types of inheritance as given below:
- Single Inheritance
- Multi-level Inheritance
- Multiple Inheritance
- Multipath Inheritance
- Hierarchical Inheritance
- Hybrid Inheritance
1. Single Inheritance
In this type of inheritance, a derived class is created from a single base class.
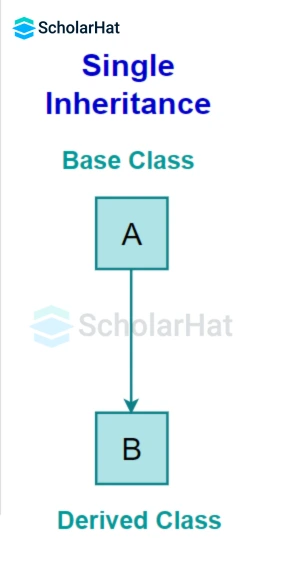
In the given figure, Class A is the parent class and Class B is the child class since Class B inherits the features and behavior of the parent class A.
Syntax for Single Inheritance
//Base Class
class A
{
public void fooA()
{
//function code:
}
}
//Derived Class
class B: A
{
public void fooB()
{
//function code:
}
}
Read More: Inheritance in C++ with Modifiers
2. Multi-level inheritance
In this inheritance, a derived class is created from another derived class.
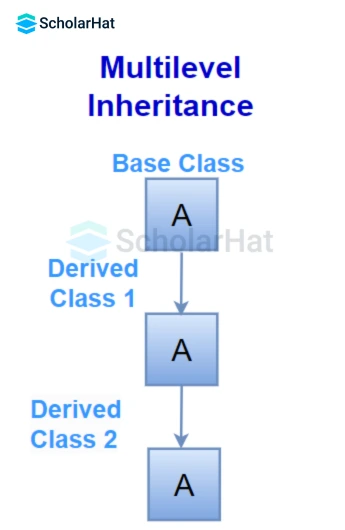
In the given figure, class C inherits the properties and behavior of class B and class B inherits from class A. So, here A is the parent class of B and class B is the parent class of C. So, here class C implicitly inherits the properties and behavior of Class A along with Class B i.e. there is a multilevel inheritance.
Syntax for Multilevel Inheritance
//Base Class
class A
{
public void fooA()
{
//TO DO:
}
}
//Derived Class
class B : A
{
public void fooB()
{
//TO DO:
}
}
//Derived Class
class C : B
{
public void fooC()
{
//TO DO:
}
}
Read More: What is Inheritance in Java: Types of Inheritance in Java
3. Multiple inheritance
In this inheritance, a derived class is created from more than one base class. This inheritance is not supported by .NET Languages like C#, F#, etc., and Java Language.
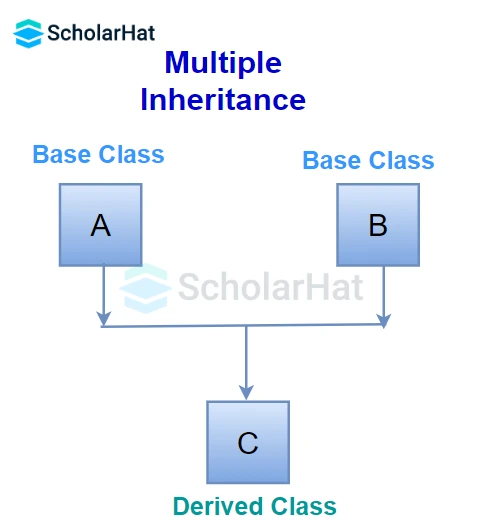
In the given figure, class C inherits the properties and behavior of classes B and A at the same level. So, here A and B both are the parent classes for Class C.
Syntax for Multiple Inheritance
//Base Class
class A
{
public void fooA()
{
//TO DO:
}
}
//Base Class
class B
{
public void fooB()
{
//TO DO:
}
}
//Derived Class
class C : A, B
{
public void fooC()
{
//TO DO:
}
}
4. Multipath Inheritance
In this inheritance, a derived class is created from other derived classes and the same base class of other derived classes. This inheritance is not supported by .NET Languages like C#, F#, etc.
In the given figure, class D inherits the properties and behavior of classes C and B. Both class C and class B inherit Class A. So, Class A is the parent for Class B and Class C as well as Class D. So it's making a Multipath inheritance.
Syntax for Multipath Inheritance
//Base Class
class A
{
public void fooA()
{
//TO DO:
}
}
//Derived Class
class B: A
{
public void fooB()
{
//TO DO:
}
}
//Derived Class
class C: A
{
public void fooC()
{
//TO DO:
}
}
//Derived Class
class D: B, C
{
public void fooD()
{
//TO DO:
}
}
5. Hierarchical Inheritance
In this inheritance, more than one derived class is created from a single base class and further child classes act as parent classes for more than one child class.
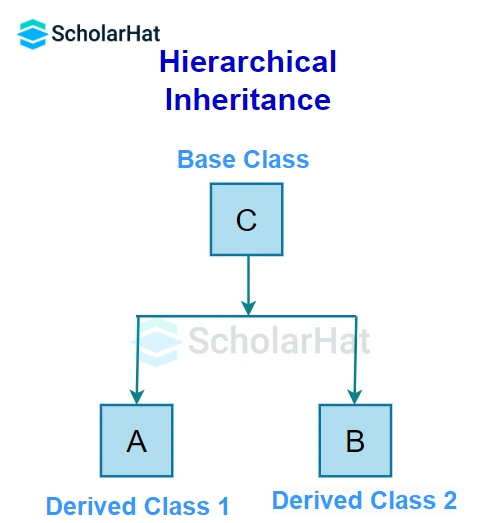
In the given figure, class C has two children class A and class B.
Syntax for Hierarchical Inheritance
//Base Class
class C
{
public void fooA()
{
//TO DO:
}
}
//Derived Class
class A: C
{
public void fooB()
{
//TO DO:
}
}
//Derived Class
class B: C
{
public void fooC()
{
//TO DO:
}
}
6. Hybrid Inheritance
This is a combination of more than one inheritance. Hence, it may be a combination of Multilevel and Multiple inheritance or a combination of Hierarchical and Multilevel inheritance.
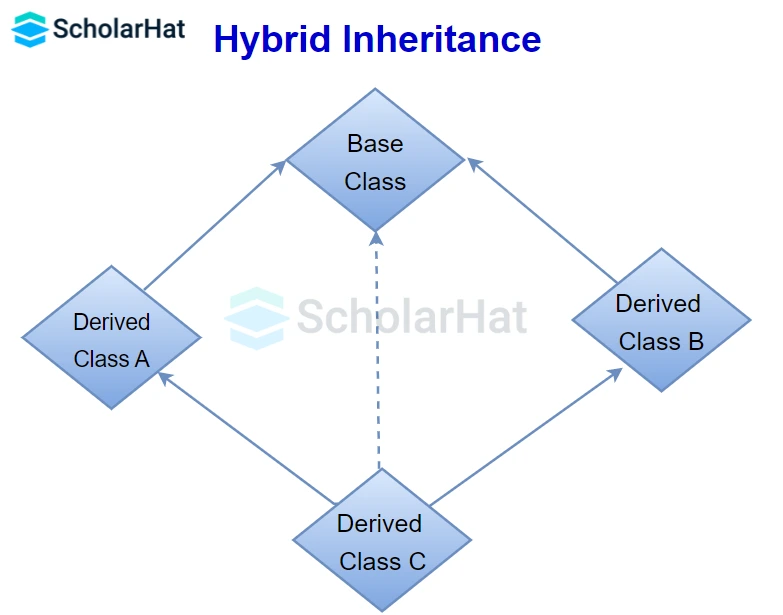
Since .NET Languages like C#, F#, etc. do not support multiple and multipath inheritance. Hence hybrid inheritance with a combination of multiple or multipath inheritances is not supported by .NET Languages.
Syntax for Hybrid Inheritance
//Base Class
class A
{
public void fooA()
{
//TO DO:
}
}
//Derived Class
class C: A
{
public void fooC()
{
//TO DO:
}
}
//Base Class
class F
{
public void fooF()
{
//TO DO:
}
}
//Derived Class
class B: C, F
{
public void fooB()
{
//TO DO:
}
}
Advantages of Inheritance
- Reduce code redundancy.
- Provides better code reusabilities.
- Reduces source code size and improves code readability.
- The code is easy to manage and divided into parent and child classes.
- Supports code extensibility by overriding the base class functionality within child classes.
- Code usability will enhance the reliability eventually where the base class code will always be tested and debugged against the issues.
Disadvantages of Inheritance
- In inheritance, both base and child classes are tightly coupled. Hence If you change the code of the parent class, it will affect all the child classes.
- In a class hierarchy, many data members remain unused and the memory allocated is not utilized. Hence it affects the performance of your program if you have not implemented inheritance correctly.
- Inheritance increases the coupling between the base class and the derived class. Any small change in the base class will directly affect all child classes that are extending the parent class.
Read More:
- Object Oriented Programming (OOPs) Concepts in C++
- OOPs Concepts in Java
- What is Class in Java? - Objects and Classes in Java
What do you think?
In this article, you learned about the different types of inheritance including advantages and disadvantages. I would like to have feedback from my blog readers. Your valuable feedback, questions, or comments about this article are always welcome.




