XAML for Xamarin.Forms
XAML is a simple and declarative markup language based on XML. It is case sensitive and strongly-typed markup language which separates presentation from business logic. XAML elements are an XML representation of CLR objects. Xaml is used to create, initialize, and set properties of an object in hierarchical relations. Xaml is mainly used for designing UI in WPF, Silverlight, Windows Phone and Xamarin Forms.
How XAML Works?
XAML files are converted into BAML (Binary Application Markup Language) then BAML will be embedded as a resource into final DLL/EXE
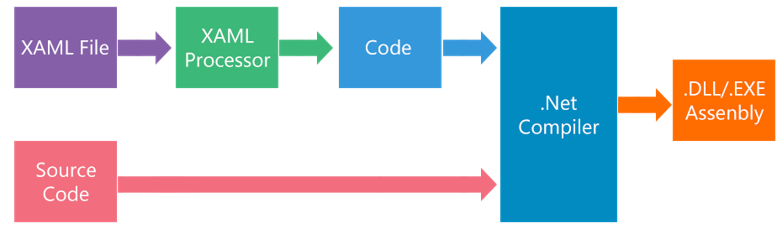
XAML Advantages
Based on XML Syntax
XAML code is short and clear
XAML code is easy to write and understand as compared to code
Designing a UI is easier with XAML as compared to code
Provides a clear separation between UI (XAML) and UI logic (C#)
Separates the roles of designer and developer
XAML vs. Code
XAML is easier to maintain and modify than equivalent code. Easily parsed and edited by software tools than equivalent code. XAML is often more concise than the equivalent C# code.

XAML has no loops, no flow control, no algebraic calculation syntax, and no event handlers. In this case, C# code helps you to define all these things.

Xamarin - XAML Page
ContentPage is a root element i.e. an opening object element xmlns is the default (Xamarin) XAML namespace. x:Class is a partial class declaration that connects markup to any code-behind defined for the partial class.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?> <ContentPage xmlns="http://xamarin.com/schemas/2014/forms" xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml" x:Class="XamarinLayouts.GridLayoutPage"> <ContentPage.Content> <Grid BackgroundColor="Yellow"> <Grid.RowDefinitions> ... </Grid.RowDefinitions> <Grid.ColumnDefinitions> ... </Grid.ColumnDefinitions> </Grid> </ContentPage.Content> </ContentPage>
XAML Properties Syntax
Attribute Syntax

Element Syntax

XAML Compilation in Xamarin
XAML can be compiled directly into IL code with the XAML compiler (XAMLC). XAMLC performs compile-time checking of XAML and notify about any errors to the user at compile-time rather than run-time. By Default XAMLC is disabled to ensure backwards compatibility but it can be enabled at both the assembly and class level by adding the XamlCompilation attribute.
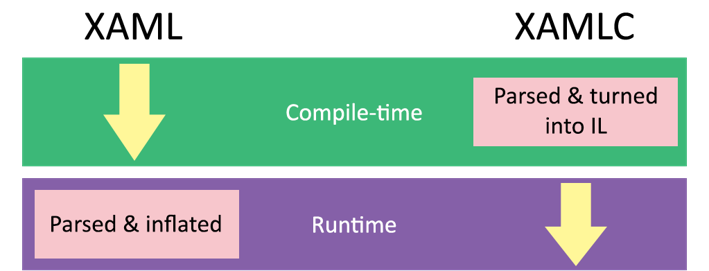
Note – Compile Option doesn't work with Resource Dictionary
XAML Markup Extensions
XAML Markup Extensions are dynamic placeholders for attribute values in XAML and resolve the value of a property at runtime. XAML Markup extensions are surrounded by curly braces { }. You can also create custom Markup extension by implementing IMarkupExtension.
Binding
Bind the values of two properties together
StaticResource
One time lookup of a resource entry from the resource dictionary
DynamicResource
Auto updating lookup of a resource entry from the resource dictionary
x:Static
Set an attribute to the value of a public static property, field, or enumeration member
x:Reference
Refer other XAML-defined types
x:Null
Set a property to null
x:Type
Set a property to a .NET Type object
x:Array
Define an array. Specify the type of the array members by setting the [Type] property to an x: Type markup extension.
What do you think?
This article is meant to be a getting started to the concept of XAML. It's meant to show the most common uses, not all of them. As you know I deliver Xamarin training at Dot Net Tricks to enable developers to learn Xamarin hands-on skills to build mobile apps.
I would like to have feedback from my blog readers. Your valuable feedback, question, or comments about this article are always welcome.
Take our free skill tests to evaluate your skill!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill test, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths.








