25
AprStrings in C++: String Functions In C++ With Example

C++ Programming For Beginners
Strings in C++:An Overview
Strings in C++ language are an arranged order of characters having a null character in the end '\0'. Strings are utilized in almost any programming language, and anyone interested in programming needs to understand them. In this C++ tutorial, we will see the various C++ string functions, their types, string classes, etc. To get a little deeper, consider our C++ Programming Course.
What is a C++ String?
A string is an object that represents a group or a sequence of characters. The string is represented as a one-dimensional array of characters and ends with a \0 (null character). Strings in C++ can be defined either using the std::string class or the C-style character arrays.
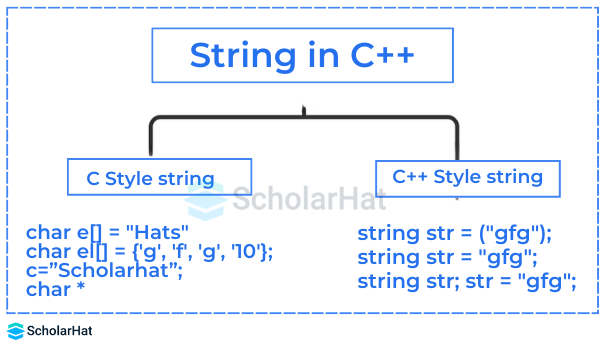
1. C-Style Character String
C-style type of strings in C++ are inherited from strings inC language. These strings are stored as an array of characters terminated by a null character ‘\0’. The first step will be to declare a string variable and then assign a value to the variable.
Syntax
data_type string_name[string_count];
Here’s an example of a string declaration in C++ :
char string[5];
Similar to arrays, you can also define strings as shown below :
char string[]=”Welcome”;
In this case, the array will hold the values “Welcome” and a null character ‘\0’ that is added to the string at the end automatically by the compiler.
Here’s a sample program in C++ Compiler for understanding the string declaration and definition.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char string[]="Welcome to ScholarHat";
cout <<string;
}
Output
Welcome to ScholarHatRead More - Advanced C++ Interview Interview Questions and Answers
2. String Class
C++ does not support any built-in string types. In the previous example, we used the array of characters terminated by a \0 to store the string value and perform operations on it (e.g., print the string value). This type of string is called the C String as it's taken from strings in c programming.
C++ offers a new string class similar to the C Strings but with efficient programming capabilities. Internally, the working of the string class is the same as C Strings (by using a character array to store the characters), while the memory definition, allocation, and addition of null characters at the end are all handled by the String class itself. In this section, we will take a detailed look into the different functions that are available as a part of the String class in C++.
While the character arrays as we have discussed above it is a statically allocated during the compile-time, while the strings are objects and hence can be dynamically allocated, Character arrays have few functions operating on them that can manipulate them. The string class has got set of various functions including the iterator functions that we will discuss in this article later on.
Syntax
std::string str("Text"); Example
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str("Welcome to ScholarHat");
cout << str;
return 0;
}
Output
Welcome to ScholarHatWays to Define a String in C++
Mainly, there are two ways to do so:
1. Using string Keyword
Syntax
string s = "Text";
string s("Text");
Example in C++ Online Editor
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s = "Welcome to ScholarHat";
string str("Welcome to ScholarHat");
cout << "s = " << s << endl;
cout << "str = " << str << endl;
return 0;
}
Output
s = Welcome to ScholarHat
str = Welcome to ScholarHat 2. Using C-style strings
Syntax
char s[] = {'t', 'e', 'x', '\0'};
char s[4] = {'t', 'e', 'x', '\0'};
char s[4] = "text";
char s[] = "text";
Example
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char s1[] = { 's', 'c', 'h', '\0' };
char s2[4] = { 's', 'c', 'h', '\0' };
char s3[4] = "sch";
char s4[] = "sch";
cout << "s1 = " << s1 << endl;
cout << "s2 = " << s2 << endl;
cout << "s3 = " << s3 << endl;
cout << "s4 = " << s4 << endl;
return 0;
}
Output
s1 = sch
s2 = sch
s3 = sch
s4 = sch
Difference between String and Character Array in C++
| Parameter | Character Array | String |
| Basic | It is a collection of variables, of character data type. | String is class and variables of string are the object of class "string" |
| Syntax | char array_name [size] | string string_name; |
| Indexing | An individual character in a character array can be accessed by its index in an array | In string, the particular character can be accessed by the function "string_name.charAt(index)" |
| Data Type | A character array does not define a datatype. | A string defines a datatype in C++. |
| Operators | Operators in C++ can not be applied to character arrays. | You may apply a standard C++ operator on the string |
| Boundary | Array boundaries are easily overrun | Boundaries will not overrun |
| Access | Fast accessing | Slow accessing |
C++ String Input Functions
In C++, there are different ways to take string inputs from the users. The way depends on the type of the string. We will look at three methods to take a string as input:
1. Using Cin
This is the most common and the easiest way to take a string-type user input
Syntax
cin>>variable_name
Example
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string s;
cout<<"Enter any String"<>s;
cin>>s;
cout<<"String is: "<Output
Enter any String
Welcome to ScholarHat
String is: Welcome to ScholarHat
2. Using getline
The getline() function in C++ is used to read a string from an input stream. It is defined in the
Syntax
getline(cin,variable_name);
Example
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s;
cout << "Enter any string" << endl;
getline(cin, s);
cout << "String is: " << s << endl;
return 0;
}
Output
Welcome to ScholarHat
3. Using stringstream
If you want to take multiple strings as input at once use the stringstream class in C++.
Syntax
stringstream stringstream_object(string_name);
Example
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s = " GeeksforGeeks to the Moon ";
stringstream obj(s);
// string to store words individually
string temp;
// >> operator will read from the stringstream object
while (obj >> temp) {
cout << temp << endl;
}
return 0;
}
Output
Welcome
to
ScholarHat
String Manipulative Functions in C++
The different string functions in the String class are :
strcpy()
strcat()
strlen()
strcmp()
strchr()
strstr()
1. strcpy(s1, s2)
This string function is a standard function of C++ that is used to copy the string s2 into string s1. We need to pass two different string values to the function strcpy() to copy the string values described below.
Example of a program illustrating strcpy()
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char string1[]="Good";
char string2[]="Morning";
strcpy(string1, string2);
cout << "The result of strcpy is : " <<string1 << '\n';
}
The result of this program will be that the value of string2 (Morning) will be copied to string1 (Good) and string2 value will be printed (Morning).
Output
The result of strcpy is : Morning
2. strcat(s1, s2)
This string function is used to append the string value or concatenate the string s2 at the end of string s1. Below is a simple example where the two string values have been passed to the function strcat().
Example of a program illustrating strcat()
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char string1[]="Good";
char string2[]="Morning";
strcat(string1, string2);
cout << "The result of strcat is : " <<string1 << '\n';
}
The result of this program will be that the value of string2 (Morning) will be concatenated to string1 (Good) and string2 value will be printed (GoodMorning).
Output
The result of strcat is : GoodMorning
3. strlen(s1)
This string function calculates and returns the length of the string s1.
Example of a program illustrating strlen()
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char string1[]="Good Morning";
cout << "The result of strlen is : " <<strlen(string1)<< '\n';
}
The result of this program will be the length of string1 which will be 12.
Output
The result of strlen is : 12
4. strcmp(s1, s2)
This string function compares the two string values and returns 0 if the two strings are the same, -1 if the value of string1<string2, and 1 when string1>string2.
Example of a program illustrating strcmp()
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char string1[]="Good";
char string2[]="Morning";
cout << "The result of strcmp is : " <<strcmp(string1, string2) << '\n';
}
The result of this program for the following input will be -1.
Output
The result of strcmp is : -6
Example of a program illustrating strcmp()
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char string1[]="Morning";
char string2[]="Good";
cout << "The result of strcmp is : " <<strcmp(string1, string2) << '\n';
}
The result of this program for the following input will be 1.
Output
The result of strcmp is : 6
Example of a program illustrating strcmp()
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char string1[]="Morning";
char string2[]="Morning";
cout << "The result of strcmp is : " <<strcmp(string1, string2) << '\n';
}
The result of this program for the following input will be 0.
Output
The result of strcmp is : 0
5. strchr(s1, ch)
This string function searches for the character in the string and returns the pointer to the first occurrence of the character.
Example of a program illustrating strchr() in C++ Editor
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char string1[]="Good Morning";
char ch = 'a';
if (strchr(string1,ch))
cout << "The character "<< ch <<" is present in the string " << string1 << '\n';
else
cout << "The character "<< ch <<" is not present in the string " << string1 << '\n';
}
The output of this program will check to see if the character ‘a’ is present in the string ‘Good Morning’. The result will be printed as :
Output
The character a is not present in the string Good Morning
If we change the character as ‘o’, it will return the pointer value of the first occurrence of the character o in the string Good Morning.
6. strstr(s1,s2)
This string function returns a pointer to the first occurrence of the string s2 in the string s1. Otherwise, the function returns a null pointer if s2 is not a part of s1.
Example of a program illustrating strstr()
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char string1[]="Good Morning. How are you?";
char string2[] = "Good Morning";
char *ptr=strstr(string1,string2);
if (ptr)
cout << string2 <<" is present in the string " << string1 << '\n';
else
cout << string2 <<" is not present in the string " << string1 << '\n';
}
The result of this program will be :
Output
Good Morning is present in the string Good Morning. How are you?
C++ Strings Iterator Functions
In C++ inbuilt string iterator functions allow the programmer to modify and traverse string elements. These functions are:
| Functions | Description |
| begin() | This function returns an iterator pointing to the beginning of the string |
| end() | This function returns an iterator that points to the end of the string |
| rfind() | This function is used to find the string’s last occurrence |
| rbegin() | This function returns a reverse iterator pointing to the end of the string |
| rend() | This function returns a reverse iterator pointing to the beginning of the string |
| cbegin() | This function returns a const_iterator pointing to the beginning of the string |
| cend() | This function returns a const_iterator pointing to the end of the string |
| crbegin() | This function returns a const_reverse_iterator pointing to the end of the string |
| crend() | This function returns a const_reverse_iterator pointing to the beginning of the string |
Example illustrating C++ Strings Iterator Functions
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// declaring an iterator
string::iterator itr;
// declaring a reverse iterator
string::reverse_iterator rit;
string s = "Welcome to ScholarHat";
itr = s.begin();
cout << "Pointing to the start of the string: " << *itr<< endl;
itr = s.end() - 1;
cout << "Pointing to the end of the string: " << *itr << endl;
rit = s.rbegin();
cout << "Pointing to the last character of the string: " << *rit << endl;
rit = s.rend() - 1;
cout << "Pointing to the first character of the string: " << *rit << endl;
return 0;
} Output
Pointing to the start of the string: W
Pointing to the end of the string: t
Pointing to the last character of the string: t
Pointing to the first character of the string: W
C++ String Capacity Functions
The C++ string capacity functions help to work with the size and capacity of the string. The primary functions of the capacity type are:
| Function | Description |
| capacity() | Returns the capacity allocated to a string by the compiler |
| resize() | Allows increasing or decreasing the size of the string |
| length() | Returns the size of the string |
| shrink_to_fit() | Decreases and makes the capacity equal to the minimum to save memory |
Example illustrating C++ String Capacity Functions in C++ Online Compiler
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s = "Welcome to ScholarHat";
// length function is used to print the length of the string
cout << "The length of the string is " << s.length() << endl;
// capacity function is used to print the capacity of the string
cout << "The capacity of string is " << s.capacity()<< endl;
// the string.resize() function is used to resize the string to 10 characters
s.resize(12);
cout << "The string after using resize function is " << s << endl;
s.resize(15);
cout << "The capacity of string before using shrink_to_fit function is "<< s.capacity() << endl;
// shrink to fit function is used to reduce the capacity of the container
s.shrink_to_fit();
cout << "The capacity of string after using shrink_to_fit function is "<< s.capacity() << endl;
return 0;
}
Output
The length of the string is 21
The capacity of string is 21
The string after using resize function is Welcome to S
The capacity of string before using shrink_to_fit function is 21
The capacity of string after using shrink_to_fit function is 15
Summary
In this detailed article, we have learned about the character array which is also called a C-style string along with the basics of the string class. String class comes with more utilities like iterator class as it’s a container class and also has discussed the variety of the string function to play with the string values. For practicals and hands-on experience, you can consider our C++ Certification program.
FAQs
Q1. What are the different string functions?
- strcpy()
- strcat()
- strlen()
- strcmp()
- strchr()
- strstr()







