Understanding Internationalization in ASP.NET MVC
Internationalization: An Overview
Internationalization is abbreviated to i18n, where 18 stands for the number of letters in the word Internationalization between the first i and last n. Internationalization is the process of developing products/software in such a way that they can be localized for languages and cultures easily. It involves Globalization and Localization. In this MVC Tutorial, we will explore more about Internationalization which will include localization and globalization in asp.net mvc, localization of validation messages, and multi-language websites in asp.net mvc. Consider our ASP.NET MVC Course for a better understanding of all MVC core concepts.
What is Globalization and Localization in Asp.net MVC?
1. Globalization
Globalization is abbreviated to G11n, where 11 stands for the number of letters in the word Globalization between the first G and last n. It is the process of developing products/software in such a way that they can support different cultures.
2. Localization
Localization is abbreviated to L10n, where 10 stands for the number of letters in the word Localization between the first L and last n. It is the process of developing products/software in such a way that they can be customized for a specific culture.
Culture in ASP.NET Framework
- ASP.NET framework has two cultures -
Culture and UICulture. Typically, these cultures' values are composed of two lower-case letters defining the language and two upper-case letters defining the locale (region). - For example, "en" represents the English language, and "GB", and "US" represent Britain and America respectively. In this way, British English is defined as "en-GB", while American English is defined as "en-US".
The Culturedetermines the results of culture-dependent functions such as date, number, and currency.The UICultureis used to locate the correct resource file and to render it for a webpage by the ResourceManager.- Every thread in .NET has CurrentCulture and CurrentUICulture properties. These properties are used by the ASP.NET globalization framework while rendering culture-dependent functions and values.
Internationalization of Validation Messages
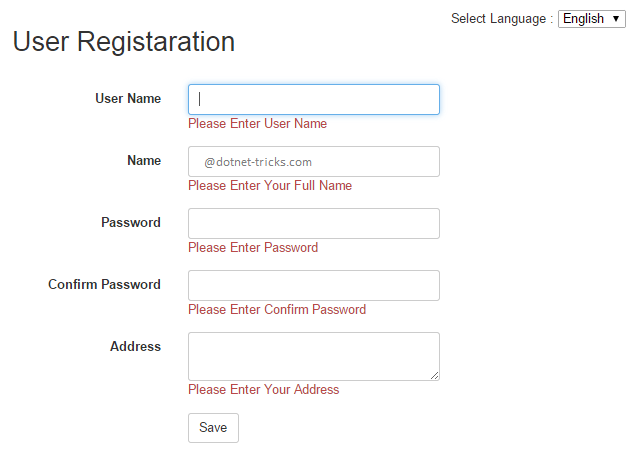
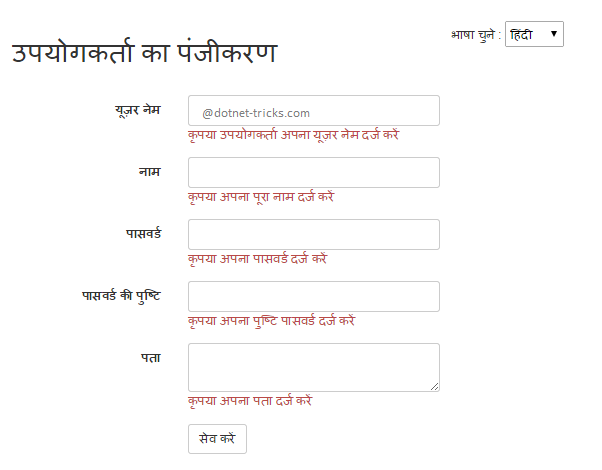
We will also see in thisHow to create multi-language websites in asp.net MVC.To make validation messages in different languages, you need to add translated messages with a key for every culture, which your application will support. In this article, I am going to add translated messages in English and Hindi. Here, the default culture is "en".
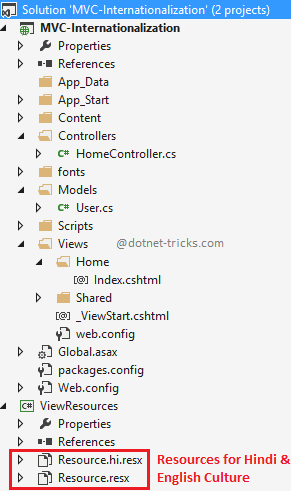
In this example, We are storing resource files for English and Hindi culture in a separate assembly, so that you can add references to that assembly in another project as well.
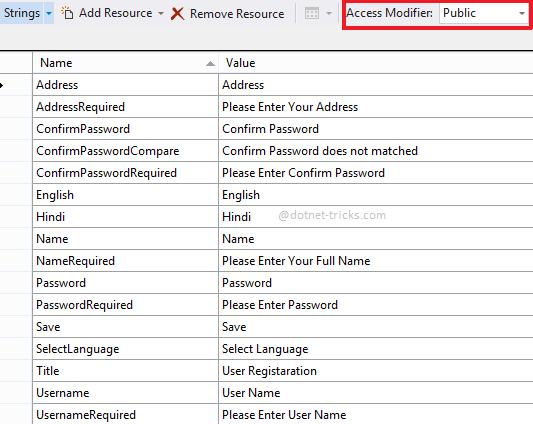
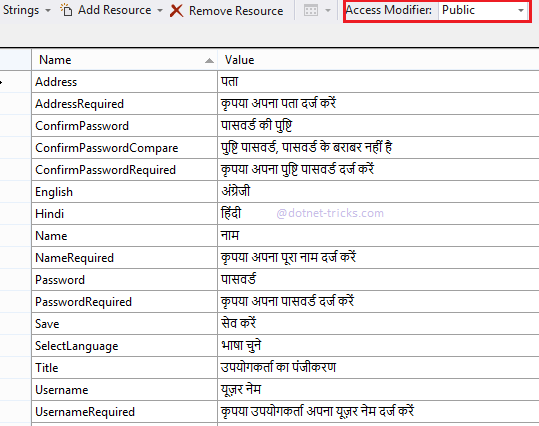
Using Resources within the ViewModel class
public class UserViewModel
{
[Display(Name = "Username", ResourceType = typeof(ViewResources.Resource))]
[Required(ErrorMessageResourceName = "UsernameRequired", ErrorMessageResourceType = typeof(ViewResources.Resource))]
public string Username { get; set; }
[Display(Name = "Name", ResourceType = typeof(ViewResources.Resource))]
[Required(ErrorMessageResourceName = "NameRequired", ErrorMessageResourceType = typeof(ViewResources.Resource))]
public string Name { get; set; }
[Display(Name = "Password", ResourceType = typeof(ViewResources.Resource))]
[Required(ErrorMessageResourceName = "PasswordRequired", ErrorMessageResourceType = typeof(ViewResources.Resource))]
public string Password { get; set; }
[Display(Name = "ConfirmPassword", ResourceType = typeof(ViewResources.Resource))]
[Required(ErrorMessageResourceName = "ConfirmPasswordRequired", ErrorMessageResourceType = typeof(ViewResources.Resource))]
[Compare("Password", ErrorMessageResourceName = "ConfirmPasswordCompare", ErrorMessageResourceType = typeof(ViewResources.Resource))]
public string ConfirmPassword { get; set; }
[Display(Name = "Address", ResourceType = typeof(ViewResources.Resource))]
[Required(ErrorMessageResourceName = "AddressRequired", ErrorMessageResourceType = typeof(ViewResources.Resource))]
public string Address { get; set; }
}
Using Resources within View
@model MVC_Internationalization.Models.UserViewModel
@{
ViewBag.Title = ViewResources.Resource.Title;
}
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-8">
<h2>@ViewResources.Resource.Title</h2>
</div>
<div class="col-md-4">
@using (Html.BeginForm("ChangeCulture", "Home"))
{
<p>
@ViewResources.Resource.SelectLanguage : @Html.DropDownList("ddlCulture", new SelectList(new[]
{
new{value="en",text=ViewResources.Resource.English},
new{value="hi",text=ViewResources.Resource.Hindi}
}, "value", "text", Session["CurrentCulture"]), new { onchange = "this.form.submit();" })
</p>
}
</div>
</div>
<br />
@using (Html.BeginForm("Index", "Home"))
{
@Html.AntiForgeryToken()
<div class="form-horizontal">
@Html.ValidationSummary(true, "", new { @class = "text-danger" })
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.Username, htmlAttributes: new { @class = "control-label col-md-2" })
<div class="col-md-10">
@Html.EditorFor(model => model.Username, new { htmlAttributes = new { @class = "form-control" } })
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.Username, "", new { @class = "text-danger" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.Name, htmlAttributes: new { @class = "control-label col-md-2" })
<div class="col-md-10">
@Html.EditorFor(model => model.Name, new { htmlAttributes = new { @class = "form-control" } })
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.Name, "", new { @class = "text-danger" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.Password, htmlAttributes: new { @class = "control-label col-md-2" })
<div class="col-md-10">
@Html.PasswordFor(model => model.Password, new { @class = "form-control" })
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.Password, "", new { @class = "text-danger" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.ConfirmPassword, htmlAttributes: new { @class = "control-label col-md-2" })
<div class="col-md-10">
@Html.PasswordFor(model => model.ConfirmPassword, new { @class = "form-control" })
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.ConfirmPassword, "", new { @class = "text-danger" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.Address, htmlAttributes: new { @class = "control-label col-md-2" })
<div class="col-md-10">
@Html.TextAreaFor(model => model.Address, new { @class = "form-control" })
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.Address, "", new { @class = "text-danger" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<div class="col-md-offset-2 col-md-10">
<input type="submit" value="@ViewResources.Resource.Save" class="btn btn-default" />
</div>
</div>
</div>
}
Setting Culture within Controller
public class HomeController : Controller
{
//initilizing culture on controller initialization
protected override void Initialize(System.Web.Routing.RequestContext requestContext)
{
base.Initialize(requestContext);
if (Session["CurrentCulture"] != null)
{
Thread.CurrentThread.CurrentCulture = new CultureInfo(Session["CurrentCulture"].ToString());
Thread.CurrentThread.CurrentUICulture = new CultureInfo(Session["CurrentCulture"].ToString());
}
}
// changing culture
public ActionResult ChangeCulture(string ddlCulture)
{
Thread.CurrentThread.CurrentCulture = new CultureInfo(ddlCulture);
Thread.CurrentThread.CurrentUICulture = new CultureInfo(ddlCulture);
Session["CurrentCulture"] = ddlCulture;
return View("Index");
}
public ActionResult Index()
{
return View();
}
[HttpPost]
public ActionResult Index(UserViewModel user)
{
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
//TO DO:
}
return View();
}
}
How it works...
Conclusion
So in this article, we have learned about localization and globalization in asp.net mvc, and localization of validation messages. I hope you enjoyed learning these concepts while programming with Asp.Net. Feel free to ask any questions from your side. Your valuable feedback or comments about this article are always welcome. Level up your career in MVC with our ASP.Net Core Certification.