Top 50 Python Interview Questions and Answers
Python Interview Questions and Answers: An Overview
Python is one of the most popular programming languages. It is very beneficial for an enthusiastic technocrat in today's world to learn Python and get access to a wide range of opportunities. In this article on Python Interview Questions and Answers, we have tried our best to provide you with some of the top Python Interview Questions and Answers.
We have segregated the questions into basic Python interview questions, intermediate Python Interview Questions, and advanced Python Interview Questions to make it easy to go through the questions. Whether you're new to Python or a seasoned pro, these questions will help you prepare effectively. Our goal is to help you understand Python better and boost your confidence for interviews. Let's dive in and explore the world of Python Interview Questions and Answers together!
Why Python?
Python's popularity stems from its readability, efficiency, and vast ecosystem. It empowers you to tackle web development, data science, machine learning, and more, making it a highly sought-after skill.
Basic Python Interview Questions for Freshers
- What is Python? What are the applications of Python?
Python is a general-purpose, high-level, interpreted programming language. The language was developed by Guido van Rossum in 1991 and further developed by the Python Software Foundation. It has a rich library that makes it applicable to building almost any type of application. It is a very simple-to-learn programming language that has a very easy syntax enhancing its code readability.
Python is an object-oriented programming language that supports modules, threads, exception-handling, automatic memory management, and third-party packages thus making it a real-world programming language capable of solving any kind of real real-world problems.
Some of the applications of Python are:
- System Scripting
- Web Development
- Game Development
- Software Development
- Complex Mathematics
- Why do we use the Python startup environment variable?
The Python startup environment variable consists of the path in which the initialization file carrying the Python source code can be executed. This is needed to start the interpreter.
- What is a dynamically typed language?
Dynamically typed language is one of the categories of typed languages. In a dynamically typed language, there is no requirement for any pre-defined data type for any variable as it is interpreted at runtime by the machine itself. In these languages, interpreters assign the data type to a variable at runtime depending on its value.
- What is a lambda function?
Lambda is an anonymous function in Python, that can accept any number of arguments, but can only have a single expression. It is generally used in situations requiring an anonymous function for a short period. Lambda functions can be used in one of the two ways:
- Assigning lambda functions to a variable:
product = lambda a, b : a * b print(mul(2, 7)) # output is 10 - Wrapping lambda functions inside another function:
def wrapperFunc(n): return lambda a : a * n prod = wrapperFunc(7) print(prod(2)) # output is 14
- What is the pass statement in Python?
Pass means not operating. The pass statement in Python is used when we cannot decide what to do in our code, but we must type something to make it syntactically correct.
def passFunc():
# does nothing
pass
myEmptyFunc() # nothing happens
- What is docstring in Python?
Python Documentation string or docstring is a multiline string used to associate documentation with a specific code segment like Python modules, functions, classes, and methods. The docstring should describe what the function or method does.
- Declaring Docstrings: The docstrings are declared using
”’triple single quotes”’or“””triple double quotes”””just below the class, method, or function declaration. All functions should have a docstring. - Accessing Docstrings: The docstrings can be accessed using the
__doc__ methodof the object or using the help function.
- What is meant by slicing in Python?
In simple terms, the word slicing means taking parts of. The slice () is used to get a part of the sequence which can be either a string, list, bytes, tuples, or any other object that follows sequence protocol.
Syntax
slice()
slice(start, stop, step)
Parameters:
- start - starting integer
- stop - integer until which the slicing takes place. At '-1' index the slicing stops.
- step - incrementing value between each index.
The slice() function returns a sliced object containing elements in the given range only.
Example
myString = 'ScholarHat'
stObject = slice(3)
print(myString[stObject])
stObject = slice(1, 5, 2)
print(myString[stObject])
Output
Sch
col
- What are built-in data types in Python?
The following are the standard or built-in data types in Python:
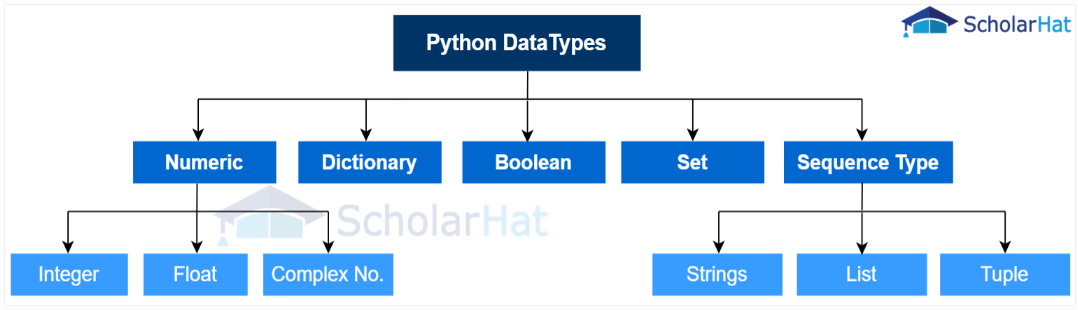
- Numeric Types: They have a numeric value. There are three different numeric types - integers, floating-point numbers, booleans, and complex numbers.
- Sequence Types: It is the ordered collection of similar or different data types. There are four basic Sequence Types -
lists,tuples,strings, andrange. - Mapping Types: In Python, hashable data can be mapped to random objects using a mapping object. There is currently only one common mapping type, the dictionary, and mapping objects are mutable.
- Set Types: A set is an unordered collection of data types that is iterable, mutable, and has no duplicate elements. The order of elements in a set is undefined.
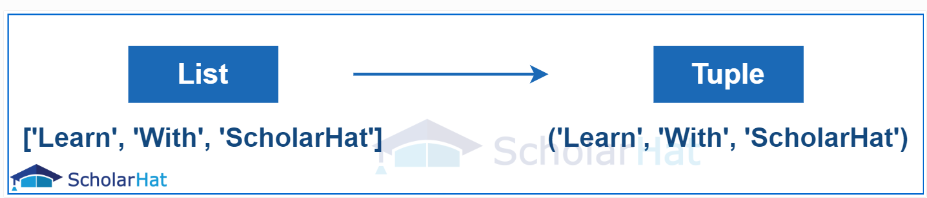
- What are lists and tuples? What is their differentiating point?
- Lists and Tuples are both sequence data types in Python that can store a collection of objects.
- The objects stored in both of them can be of various data types.
- Lists are represented using square brackets
[], while tuples are represented using parentheses(). - The differentiating point is that while lists are mutable, tuples on the other hand are immutable objects. This means that lists can be modified, appended, or sliced on the go but tuples remain constant and cannot be modified in any manner.
tup = ('scholarhat',3, 6.7)
lis = ['scholarhat',3, 6.7]
print(tup[0]) # Output: 'scholarhat'
print(lis[0]) # Output: 'scholarhat'
tup[0] = 'dotNet' # TypeError: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment
lis[0] = 'ansh'
print(tup[0]) # output: 'scholarhat'
print(lis[0]) # output => 'dotNet
- Are access specifiers used in Python?
No, python does not make use of access specifiers like private, public, protected, etc. It uses the access specifiers in the form of single (protected) _ or double underscore (private) __ as prefixed to the variable names. By default, the variables without prefixed underscores are public.
class Employee:
# protected members
_emp_name = None
_age = None
# private members
__emp_id = None
# constructor
def __init__(self, emp_name, age, emp_id):
self._emp_name = emp_name
self._age = age
self.__emp_id = emp_id
# public member
def display():
print(self._emp_name +" "+self._age+" "+self.__emp_id)
- What are iterators in Python?
Iterators are objects with which one can iterate over iterable objects like lists, strings, tuples, etc. Python iterator implements __itr__() and the next() method to iterate the stored elements.
- __iter__() method initializes an iterator.
- __next__() method returns the next item in iteration and points to the next element. Upon reaching the end of iterable object __next__() must return
StopIterationexception.
- Is it possible to use break and continue together in Python? How?
Yes, you can use both break and continue together in a Python loop. The break will stop the current loop from execution, while the continue will take it to another loop.
for i in range(1, 11):
if i % 2 == 0:
continue # Skip even numbers
if i == 7:
break # Exit the loop when i is 7
print(i)
- What are generators in Python?
Generators in simple language are a way to create iterators. Any function that can return an iterator object and we can iterate one value at a time is a generator. We already know about iterator and its methods: - __iter__() and __next__(). They employ the use of yield keyword rather than return to return a generator object.
As generators are iterator functions, we need not create these methods so, that extra overhead is saved. These methods are to keep track of internal states and raise Stop Iteration when no values are left. This all overhead can be taken care of with the help of generators. All overhead mentioned is taken care of by generators.
- What is the difference between a set and a dictionary?
- The
setis an unordered collection of data types that is iterable, mutable, and has no duplicate elements. - A dictionary in Python is an ordered collection of data values, used to store data values like a map.
- What is the use of self in Python?
Self is an instance of a class or an object in Python. It is included as the first parameter. It helps differentiate between the methods and attributes of a class with local variables.
- What is the difference between a mutable datatype and an immutable data type?
- Mutable data types can be modified i.e., they can change at runtime. Eg –
List,Dictionary, etc. - Immutable data types can not be modified i.e., they can not change at runtime. Eg –
String,Tuple, etc.
- What is PEP 8?
PEP stands for Python Enhancement Proposal which is an official design document providing information to the Python community, or describing a new feature for Python or its processes. PEP 8 is a style guide for Python language. It’s a guide to writing how to style your code to make it more readable. With multiple developers, there will be a large code base and every developer follows the same styling which will maintain the uniformity in code.
- Is indentation required in Python?
Indentation is a very important aspect of Python syntax. If not done properly, the code is not executed properly and might throw errors. Indentation is usually done using four space characters.
- Can we pass a function as an argument in Python?
Yes, we can pass any number of arguments to a function, including objects, variables (of the same or distinct data types), and functions. Functions can be passed as parameters to other functions because they are objects. Higher-order functions are functions that can take other functions as arguments.
- Can we reverse a list in Python?
Yes, we can reverse a list in Python using the reverse() method. The code is as follows:
def reverse(s):
str = ""
for i in s:
str = i + str
return str
Intermediate Python Interview Questions
- What is the init method in Python?
__init__: Reserved method in Python classes. It is similar to writing a constructor in other object-oriented languages. This method is called when you create an instance of a class and you can pass parameters that will be used to initialize the attributes.
Usage: A class named Car is there. A car has some basic attributes like "color", "company", "top speed", "mileage" etc.
class Car(object):
def __init__(self, name, domain, color, speed):
self.name = name
self.domain = domain
self.color = color
self.speed = speed
def create_car(self):
print("car created")
car1 = Car("honda city", "racing", "red", 200)
car2 = Car("Numberica", "cab", "white", 180)
__init__ method to initialize the instance of the car class. self points or can be used to access the instance of the class. It maps and ties the attributes with the given arguments.
- What is the difference between .py and .pyc files?
- .py files are Python source files whereas .pyc files are compiled bytecode files generated by the Python compiler.
- Before executing a python program python interpreter checks for the compiled files. If the file is present, the virtual machine executes it. If not found, it checks for .py file. If found, compiles it to .pyc file, and then the python virtual machine executes it.
- Having a .pyc file saves you the compilation time.
- What are Python namespaces? Why are they used?
A namespace in Python ensures that object names in a program are unique and can be used without any conflict. Python implements these namespaces as dictionaries with 'name as key' mapped to a corresponding 'object as value'. This allows for multiple namespaces to use the same name and map it to a separate object. A few examples of namespaces are as follows:
- Local Namespace includes local names inside a function. This namespace is temporarily created for a function call and gets cleared when the function returns.
- Global Namespace includes names from various imported packages/ modules that are being used in the current project. This namespace is created when the package is imported into the script and lasts until the execution of that script.
- Built-in Namespace includes built-in functions of core Python and built-in names for various types of exceptions.
- How Python is interpreted?
- Python as a language is not interpreted or compiled. Interpreted or compiled is the property of the implementation. Python is a bytecode(set of interpreter readable instructions) interpreted generally.
- The source code is a file with
.pyextension. - Python compiles the source code to a set of instructions for a virtual machine. The Python interpreter is an implementation of that virtual machine. This intermediate format is called
bytecode. - .py source code is first compiled to give .pyc which is bytecode. This bytecode can be then interpreted by the official CPython or JIT(Just in Time compiler) compiled by PyPy.
- How lists and tuples are different?
These are the following differences between a list and a tuple:
| Lists | Tuples |
| Lists contain mutable elements where we can manipulate and perform operations on existing elements. | Tuples are immutable so they are not attached to many methods to manipulate the contents as a result they are faster in execution. |
| Lists are good at reduced memory utilization. | memory utilization is not good as compared to the list. |
| Lists are considered to be slower than tuples | Tuples are considered to be faster as compared to lists. |
- Can we call a parent class without its instance creation?
Yes, we can call a parent class without its instance creation if the base class is instantiated by other child classes or if the base class is a static method.
- Differentiate between Python arrays and lists?
In Python, the main difference between arrays and lists is, that an array can only hold a particular data type whereas in a list we can add different types of elements. If we want to use an array, we need to import array module because they are not included in Python's fundamental data types. You need to include typecode in the declaration of an array which will tell Python which data type it would be holding. Such rules are not with the list data type.
- How is memory management done in Python?
Python uses its private heap space to manage the memory. All the objects and data structures are stored in the private heap space. Even the programmer can not access this private space as the interpreter takes care of this space. Python also has an inbuilt garbage collector, which recycles all the unused memory, frees the memory, and makes it available to the heap space.
- How does multiple inheritance work in Python?
Python also supports multiple inheritance as other object-oriented programming languages. You can specify all the classes from which you are inheriting comma-separated fashion.
Example in Python Online Compiler
class Parent1(object):
def __init__(self):
self.str1 = "Person1"
print("Parent 1")
class Parent2(object):
def __init__(self):
self.str2 = "Person2"
print("Parent 2")
class Child(Parent1, Parent2):
def __init__(self):
# Calling constructors of Parent1 and Parent2 classes
Parent1.__init__(self)
Parent2.__init__(self)
print("Child")
def print_str(self):
print(self.str1, self.str2)
ob = Child()
ob.print_str()
Output
Parent 1
Parent 2
Child
Person1 Person2
- How to delete a file in Python?
In Python, we can delete a file using os. unlink() or os.remove().
import os
os.unlink(filename) or
os.remove (filename)
- What is pickling and unpickling?
- Pickling in Python means serializing an object structure. It's a way of converting Python data structures like lists, dictionaries, and tuples into character streams. The character streams would have all the necessary information to reconstruct the object. pickle.dump() function is used for this.
- Unpickling is deserialization or you can say the reverse of pickling. It deserializes the byte stream to recreate the objects stored in the file and loads the object to memory. pickle.load() function is used for this.
- What are help() and dir() functions in a Python program?
help() - Every built-in function in Python has a documentation string attached to it which we can view using the help() function. We can write documentation strings to user-defined functions and that can also be read by the help() function. The use of the documentation string makes the program more readable to others.
dir() - We all know the concept of namespace. Let's say you want to see all the names that are defined in your program. If you call dir() without arguments it will return a list of names which all are in an interactive namespace.
x = 1
y = "python"
dir()
# output: ['__builtins__', '__doc__', '__name__', '__package__', 'x', 'y']
import datetime
dir(datetime)
# output: ['MAXYEAR', 'MINYEAR', '__doc__', '__name__', '__package__', 'date', 'datetime', 'datetime_CAPI', 'time', 'timedelta', 'tzinfo']
- How arguments are passed in Python?
In Python, arguments are passed by reference, i.e., reference to the actual object is passed. We cannot change the value of the references. However, you can change the object if it is mutable. Let's see the working in Python Compiler.
Example
def appendNumber(arr):
arr.append(4)
arr = [1, 2, 3]
print(arr)
appendNumber(arr)
print(arr)
Output
[1, 2, 3]
[1, 2, 3, 4]
- What is meant by *args and **kwargs?
*argsis a special syntax used in the function definition to pass variable-length arguments. * means variable length and “args” is the name used by convention. You can use any other. When you use '*' with an argument it becomes iterable means you can iterate over it and execute some logic or some high-order functions like map or filter.def printAll(*args): for arg in args: print(arg) printAll('Hello', 'Welcome', 'to', 'ScholarHat')Output
Hello Welcome to ScholarHat- The
**kwargssyntax is used to pass a keyworded, variable-length argument list to a function. A keyworded argument means a variable that has a name when passed to a function. It’s like you are sending a dictionary to a function where it can get values using keys.def printAllkwargs(**kwargs): for key, value in kwargs.items(): print('%s == %s' % (key, value)) # Call Function printAllkwargs(first='First', mid='Mid', last='Last')Output
first == First mid == Mid last == Last
Read more about arguments for a function in Python Functions
- How do you do data abstraction in Python?
Data Abstraction provides only the required details and hides the implementation from the world. It can be achieved in Python by using interfaces and abstract classes.
Python Interview Questions For Experienced Developers
- Differentiate between a package and a module in Python.
A module in Python is a single file that you can import into your Python program and use by using the import keyword followed by the filename. A package is a collection of modules which means it contains more than one Python module. Packages can be nested up to any depth with directories containing a special file called __init__.py.
Modules are created and used when you want to share small code of functions everywhere in your project. Suppose you have a bunch of functions querying the database so you can put them all in one place and import that file wherever you want.
- What is the use of finalize?
The finalize() method is used for freeing up unmanaged resources and clean up before the garbage collection method is invoked. This helps in performing memory management tasks.
- How to achieve multithreading in Python?
Python gives you a multi-threading package and you can use it, but it’s not considered a good idea. Python has a package that has the construct, Global Interpreter Lock (GIL). GIL makes sure that only one thread executes at a time and then it will switch to another thread.
The switching between the threads may seem like multithreading but it’s just faster switching which the human eye can't recognize and we think like they are getting executed parallelly. But all will be executing the same CPU core.
This switching puts extra overhead in code execution. So, if you are thinking of speeding up your code with Python's threading library then it's not a good idea.
- What are custom errors in Python?
Python has a good amount of built-in functions to generate exceptions. But sometimes you are required to raise some custom exceptions. To create your custom exception, you need to derive the indirectly or directly from the Exception class. Built-in exceptions are derived from the Exception class. When developing a large Python application it's a good practice to define all your user-defined exceptions in Exception.py or errors.py file.
The most widely used standard to define User-defined Exceptions is creating a base class and inheriting all other exceptions from that class.
Example
We will create a user-defined exception in the Python Editor that will raise an error if the value is lower than expected or bigger than expected.
# Define Python user-defined exceptions
class Error(Exception):
"""Base class for other exceptions to inherit from"""
pass
class ValueSmallError(Error):
"""Raised when the input value is small"""
pass
class ValueLargeError(Error):
"""Raised when the input value is large"""
pass
# The number to be guessed
value = 15
while True:
try:
num = int(input("Guess a number: "))
if num < value:
raise ValueSmallError
elif num > value:
raise ValueLargeError
break
except ValueSmallError:
print("This value is smaller than the number, try again!\n")
except ValueLargeError:
print("This value is larger than the number, try again!\n")
print("Congratulations! You guessed the value correctly.")
Output
Guess a number: 12
This value is smaller than the number, try again!
Guess a number: 18
This value is larger than the number, try again!
Guess a number: 15
Congratulations! You guessed the value correctly.
Discover more about errors and exceptions in Python in Exception Handling in Python
- What is PIP?
PIP stands for Python Installer Package. As the name indicates, it is used for installing different Python modules. It is a command-line tool providing a seamless interface for installing different Python modules. It searches over the internet for the package and installs it into the working directory without the need for any interaction with the user.
Syntax
pip install
- How can you generate random numbers in Python?
- Python provides a module named
randomusing which we can generate random numbers. - We have to import a random module and call the
random()method as shown below. Therandom()method generates float values lying between 0 and 1 randomly.import random print(random.random()) - If you want to generate customized random numbers between specified ranges, you can use the
randrange()methodSyntax
randrange(beginning, end, step)Example
import random # Generate a random odd number between 10 and 99 random_number = random.randrange(10, 100, 2) # Print the random number print(random_number)
- What is a negative index in Python and where to use them?
The data structures that support indexing also support negative indexing. In general, 0 is an index for the first element in the sequence then 1 for the next, and so on. Same for the negative index, -1 represents the last element index, -2 for the element before that, and so on.
A negative index is useful in many ways. One of the ways is if you want to extract the last element of the sequence and don't know the size you can simply use the negative index and get the last element. Even to loop the sequence in reverse we can use the negative indexes.
Example
Str1 = "ScholarHat"
print(Str1[-1])
Output
t
- Write a program for counting the number of every character of a given text file.
import collections
import pprint
with open("sample_file.txt", 'r') as data:
count_char = collections.Counter(data.read().upper())
count_value = pprint.pformat(count_char)
print(count_value)
- Do runtime errors exist in Python? Give an example.
Yes, runtime errors exist in Python.
Example
print "ScholarHat"
Output
SyntaxError: Missing parentheses in call to 'print'. Did you mean print("ScholarHat")?
- Whenever Python exits, not all the memory is deallocated. Why is it so?
Upon exiting, Python’s built-in effective cleanup mechanism comes into play and tries to deallocate or destroy every other object. However, Python modules that have circular references to other objects, or the objects that are referenced from the global namespaces, aren’t always deallocated or destroyed. This is because it is not possible to deallocate those portions of the memory that are reserved by the C library.
- What is the difference between generators and normal functions?
There are the following differences between generators and normal functions:
| Scope | Generator | Normal |
| Execution | They can be paused in the middle of execution and resumed | They run to completion and return a value |
| Return value | They can return multiple values through multiple iterations. | They return a single value (or none) |
| Memory usage | They keep the current value in memory, | They create a large amount of memory overhead |
| Usage | They are used to generate values that can be iterated over. | They are used when we have to perform a task and return a result. |
- What are the advantages of using Numpy over nested List in Python?
There are the following advantages of using Numpy over a nested list:
- Python lists are general-purpose data containers and are very efficient. They support easy insertion, deletion, appending, and concatenation with a list. List comprehension techniques let us create new lists and manipulate them effectively.
- But there are some things that they don't support like 'vectorized' operations: - element-wise multiplication, addition, finding mean, standard deviation, and many other statistical operations.
- Lists can store data of different types for which Python has to remember their types and handle each element with different code according to their types
- Numpy is more efficient than lists and more convenient. You can easily apply financial, statistical, and vector-matrix operations, which saves lots of code and effort.
- You get faster and more efficient operations with NumPy like fast searching, basic statistics, algebra, histograms, etc.
- Write a Program to combine two different dictionaries. While combining, if you find the same keys, you can add the values of these same keys. Output the new dictionary
from collections import Counter
d1 = {'key1': 78, 'key2': 120, 'key3': 500}
d2 = {'key1': 200, 'key2': 400, 'key4': 300}
new_dict = Counter(d1) + Counter(d2)
print(new_dict)
- Differentiate between new and override modifiers.
- The
newmodifier is used to instruct the compiler to use the new implementation and not the base class function. - The
Overridemodifier is useful for overriding a base class function inside the child class.
- Explain the Dogpile effect.
The dogpile effect is when the cache expires, and websites are hit by multiple requests made by the client at the same time. Using a semaphore lock prevents the Dogpile effect. In this system, when a value expires, the first process acquires the lock and starts generating a new value.
Summary
We all know that Python is one of the most highly used programming languages. It is a rich source of libraries and is thus used in futuristic technologies and domains like game development, AI, Machine learning, and, Data Science. It simplifies your multiple lines of code into just a few lines. This article has covered the commonly asked interview questions. It will help you crack various job interviews related to Python development, Data science, Machine learning, etc.
FAQs
Q1. How should I prepare for a Python programming interview?
Q2. What types of questions can I expect in a Python interview?
Q3. What are the different categories of Python interview questions?
- Basics: Covers fundamental syntax, data types, variables, operators, and control flow.
- Data Structures and Algorithms: Probes your understanding of lists, tuples, dictionaries, sets, functions, loops, and common algorithms.
- Object-Oriented Programming (OOP): Tests your knowledge of classes, objects, inheritance, polymorphism, and encapsulation.
- Modules and Packages: Evaluates your ability to import, use, and create modules.
- Exception Handling: Assesses your skills in handling errors and exceptions.
- Frameworks and Libraries: If relevant, expects questions on specific frameworks like Django, Flask, or Pandas.
Q4. What are some common mistakes candidates make in Python interviews?
- Not understanding the Pythonic way of doing things: Python prioritizes readability and elegance.
- Confusing mutable and immutable data types: Grasping the difference between lists and tuples is crucial.
- Struggling with built-in functions and modules: Utilize Python's vast ecosystem effectively.
- Poor code quality: Write clean, well-commented, and efficient code.
- Being overly reliant on memorized answers: Focus on understanding and explaining your thought process.